KEYWORDS: Self Driving Trucks, Autonomous Driving, Case Study Solutions, AI Data, Dataset, Auto-driving Dataset
According to FreightWaves, an industry analyst firm, trucking accounts for 43% of total logistics costs worldwide, with a total value of $4.1 trillion, a figure that is expected to reach $5.5 trillion by 2027. [1]
Within the U.S., trucks move about 70 percent of freight. There are over 20 states in the U.S. that allow the commercial use of intrastate autonomous trucks, and they’re already on the road in some places.
Currently, some of the world’s well-known self-driving trucking companies are Aurora Innovation (AUR), Embark Technology (EMBK), TuSimple (TSP), Plus, Gatik, Torc Robotics, etc.
As Richard Steiner, head of policy and communications for self-driving truck firm Gatik said, “Over the next few years, you’re definitely going to see autonomous trucks become increasingly commonplace across multiple markets.”[2]
1. The Potential Benefits of Autonomous trucks
1.1 Addressing the shortage of truck drivers
Self-driving trucks have a remarkable role to play in addressing the truck driver shortage in the freight transportation industry.
According to the American Transportation Research Institute, the driver shortage is a major constraint in the coming years, with the trucking industry expected to be short 160,000 drivers by 2030 [3].
But with the help of self-driving trucks, this problem will be greatly alleviated.
Autonomous driving offers the opportunity to reallocate labor to more productive tasks. For example, truck drivers may have more options and less risk on the road.
In addition, drivers can become dispatchers and responders when self-driving trucks encounter problems on the road.
1.2 Providing safer, more efficient, and lower costs
The World Health Organization estimates that more than 1.3 million people are killed on roadways globally each year.
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, 94 percent of motor vehicle crashes are related to driver factors, such as drowsy, distracted, or illegal driving[4].
In this case, self-driving trucks will be able to perform their tasks with precision and won’t suffer from issues such as human fatigue and distracted driving, further improving road safety.
In fact, California-based Gatik has already commercialized self-driving trucks. It now operates fully driverless trucks for Walmart (WMT) in Arkansas and Canadian grocery and pharmacy retailer Loblaw in Ontario.
Self-driving trucks don’t need to take breaks like human drivers, which means they can travel longer distances in less time and can operate 24/7.
Meanwhile, self-driving trucks will potentially be more efficient than humans in terms of vehicle operation, especially acceleration and braking, resulting in lower fuel consumption per mile.
According to McKinsey, full truck autonomy would reduce operating costs by about 45%, saving the U.S. industry $85 billion to $125 billion annually[5].
2. The Challenges of Self-Driving Trucks
The challenge for self-driving trucks is to operate in all types of weather and road conditions.
In sunny conditions, self-driving trucks can certainly perform well. However, when it comes to dark conditions and harsh sunlight, as well as harsh conditions such as fog, rain, storms, and snow, how to perform well is the more important issue to solve.
In addition, since most trucks will be traveling on highways, it is important to be able to quickly recognize and react to road signs and road conditions at high speeds. This is another crucial challenge for self-driving trucks.
As we know, self-driving trucks can’t react to weather and road conditions without being fed a large amount of high-quality AI training data.For in-depth insights into how this data plays a pivotal role in autonomous driving, check out the comprehensive solutions at maadaa.ai’s Autonomous Driving main page which includes detailed data annotation methods and tools.
So how does AI data affect automated trucks? The following case study may give you some insight.
3. A practical case study of autonomous freight trucking
The following case study will help to understand more about self-driving trucks.
This case is published with permission from maadaa.ai, a company dedicated to providing professional, agile, and secure data products and services to the global AI industry.
Client: A well-known leading logistics company
Background:
The logistics Company seeks to harness automated driving technology to optimize its long-haul freight business, aiming for enhanced efficiency and cost reduction.
Challenge:
Trucks present unique challenges due to their size and weight, making the technical demands for automated driving more stringent.
High-speed highway driving and frequent lane changes present algorithmic challenges.
Trucks must accurately identify road signs on highways to ensure the correct choice of exits and routes.
Solution:
We provided the client with truck-specific data collection and annotation services, emphasizing:
Highway Scenarios: Since trucks primarily operate on highways, we focused on gathering comprehensive data from highway conditions.
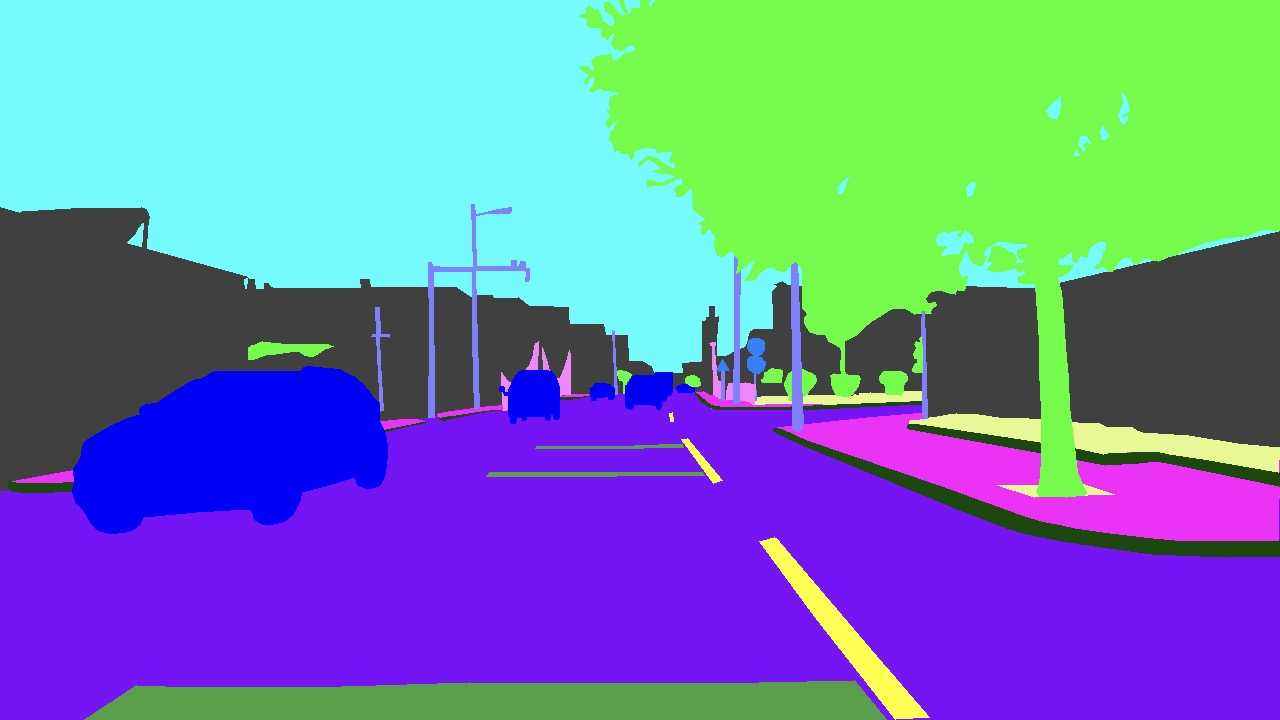
Lane Label Annotation: Detailed annotation of highway lane masks was performed to ensure that trucks could accurately identify and switch lanes. Labels included fast lanes, slow lanes, emergency stops, and other highway-specific lane information.
Sign Relations: Emphasis was placed on annotating highway exit signs, distance indications, and other crucial information. We meticulously annotated the relations between signs associated with the highway.
Result:
With our data collection and annotation services and the expertise of our data specialists in the field of autonomous driving, the logistics company was able to train its models more efficiently.
Part of the success was attributed to the diverse range of datasets we offer:
· Road and Lane Segmentation for precise navigation
Lane Line Segmentation Dataset
Lane Merging and Fork Area Segmentation Dataset
Long Lane Line Contour Segmentation Dataset
· Weather and Lighting Condition Datasets to ensure reliability under various environmental scenarios
Sunny Day City Road Dash Cam Video Dataset
Cloudy Day City Road Dash Cam Video Dataset
Low lighting Dash Cam Video Dataset
· Traffic Scene Understanding for safe and efficient driving
Dashcam Traffic Scenes Semantic Segmentation Dataset
CCTV Traffic Scene Semantic Segmentation Dataset
Traffic Sign Relationships Dataset
· Vehicle and Driving Behavior Datasets crucial for predicting future actions and ensuring safe interactions
Vehicle Driving Behaviors Video Dataset
· Advanced Road Understanding for handling complex driving scenarios
Further reading:
[maadaa.ai Case Study] Self-Driving Cars Empowering by Real-World Data
Reference List:
- https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20201111005380/en/Global-Freight-Trucking-Market-Report-2020---Market-to-Reach-5.5-Trillion-by-2027---ResearchAndMarkets.com
- https://www.investors.com/news/technology/autonomous-trucks-are-coming-but-face-bumpy-road/
- https://www.ajot.com/news/the-truck-driver-shortage-in-the-us-continues#:~:text=The%20Shortage%20of%20Truck%20Drivers&text=According%20to%20a%20recent%20study,shortage%20of%20160%2C000%20truck%20drivers.
- https://www.taproot.com/is-human-error-the-cause-of-vehicle-accidents/#:~:text=Automated%20vehicles'%20potential%20to%20save,are%20due%20to%20human%20error.
- https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/travel-logistics-and-infrastructure/our-insights/distraction-or-disruption-autonomous-trucks-gain-ground-in-us-logistics